What is an endoscopic biopsy?
An endoscopic biopsy is a medical procedure conducted to gather a small piece of tissue from the body using a medical instrument called an endoscope. This tool is a thin and flexible tube with light and a camera on one end, which allows doctors to directly visualise and access internal organs or tissues without the need for more invasive surgical methods. The sample of tissue collected will be looked at closely with the help of a microscope to identify conditions like cancer, infection, inflammation, and other irregularities.
What are the common conditions diagnosed with endoscopic biopsies?
Endoscopic biopsies serve as an essential diagnostic technique for identifying and verifying different medical conditions by procuring tissue samples from various areas of the body. This less invasive procedure aids in the timely recognition and control of numerous diseases, enhancing patient results and informing suitable treatment approaches.
Common conditions diagnosed with endoscopic biopsies include gastrointestinal disorders, cancers, infections, respiratory conditions, liver diseases, gynaecological conditions, and autoimmune disorders.
Gastrointestinal disorders
Endoscopic biopsies are important because they offer a less invasive way to diagnose, keep track of, and control different conditions in the digestive system, which results in better outcomes for patients.
Gastric ulcers and gastritis
Ulcers are inflammations or sores in the stomach lining. The biopsy assists in detecting ulcers or inflammation and determining their severity, directing treatment to avoid bleeding or perforation issues.
Coeliac disease
An autoimmune disorder affecting the small intestine and the diagnosis is confirmed by identifying damage to the intestinal villi, which is crucial for beginning a gluten-free diet to treat the condition.
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
For inflammatory medical conditions like Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, using an endoscopy can determine the type and severity of inflammation, helping to tailor treatment plans and maintain remission.
Polyps
Endoscopic procedures are crucial for the early detection of polyps and other gastrointestinal abnormalities in the colon and rectum, allowing for prompt treatment and reducing the risk of colorectal cancer.
Respiratory conditions
Endoscopic biopsies are essential for diagnosing respiratory disorders by directly examining lung and bronchial tissues, offering precise diagnoses with minimal invasiveness, and guiding effective treatment.
Lung cancer
Endoscopic biopsies are crucial for determining lung cancer type and stage. By sampling suspect lesions in the lungs or bronchi, they verify cancer cells and assess the spread, guiding tailored treatment plans.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
Biopsies evaluate the existence of complications like bronchitis or emphysema. Biopsies can help rule out conditions that mimic COPD symptoms and provide an understanding of airway and lung tissue damage.
Pulmonary fibrosis
Essential for diagnosing pulmonary fibrosis, idiopathic, occupational exposure, and autoimmune forms. They extract lung tissue samples to identify scarring, crucial for treatment and managing progression.
Tuberculosis
Valuable for obtaining lung tissue samples when tuberculosis (TB) is suspected. They confirm the presence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and help identify drug-resistant strains, guiding effective treatment.
Urinary tract conditions
Biopsies are minimally invasive procedures and essential for diagnosing urinary tract disorders to view and sample tissues from the bladder, urethra, ureters, and kidneys, which aids in diagnosis and treatment.
Bladder cancer
Biopsies collect sample tissue from bladder lesions to confirm cancer presence, and determine cancer type, grade, and stage. This informs targeted treatment plans involving surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation.
Kidney stones
Biopsies can directly sample ureter or renal pelvis tissue to detect kidney stones and exclude conditions like tumours or strictures. Biopsies clarify the causes of stone formation, ensuring diagnosis.
Interstitial cystitis
Biopsies examine the bladder lining for chronic inflammation signs. They exclude conditions like bladder cancer or infections, providing insights into inflammation and damage for effective treatment decisions.
Prostate conditions
Biopsies confirm conditions like BPH and prostate cancer by sampling tissue from the gland. They assess cancer presence, and stage, and guide treatment decisions such as surgery, radiation, or hormone therapy.
Gynaecological conditions
Endoscopic biopsies are crucial in gynaecology for diagnosing and managing various reproductive system disorders, doctors can visualise and sample tissues from the cervix, uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes.
Cervical cancer
Endoscopic biopsies use a tool known as a colposcope for a thorough examination of the cervix collecting tissue pieces from doubtful spots and providing the confirmation of precancerous or cancer cells.
Endometrial cancer
Biopsies in diagnosing endometrial cancer come from their ability to find out if there are any irregular or malignant cells present, which is important for ranking the disease and deciding on treatments.
Ovarian cysts
Endoscopic biopsies help visualise, outline and differentiate if an ovarian cyst is benign or malignant, find out endometriomas or other pathologies and guide the plan for surgery or medical treatment plans.
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
Biopsies confirm PID diagnosis by proving there is infection or inflammation in the reproductive organs, exclude other situations like ectopic pregnancy or ovarian torsion and help decide on suitable treatment.
What are the benefits of endoscopic biopsies?
Endoscopic biopsies are an advisable choice for diagnosis compared to traditional methods. They provide less invasive procedures that give more precise results quickly and with fewer risks involved. This promotes faster recovery time for patients. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) research on the safety of doing multiple mucosal biopsies affirms that these procedures are effective and safe even in complex cases or research environments.
Biopsies done through endoscopy are less invasive compared to regular surgery biopsies, causing smaller cuts, less pain and quicker recovery. This is shown in a study by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), where 253 endoscopic procedures with biopsies had no major complications and only a few minor issues at a rate of 5.1%.
The use of endoscopes helps to see the target area in real time. This makes sure that tissue samples are taken from spots that are most related and doubtful, enhancing accuracy and lessening the chances of missing pathology areas.
As endoscopic biopsies are less invasive, they usually show fewer complication rates like infections or notable bleeding. In the NIH study, there were no major complications and small issues such as self-limited bleeding and pain happened rarely but were manageable. Many endoscopic biopsies can be done as an outpatient process, enabling patients to return home on the same day and not requiring extended hospital stays. The data from the NIH study about 253 procedures backs up that these outpatient biopsies are safe and doable.
Direct visualisation and targeted sampling are likely to diminish the chance of overlooking pathologic areas, which can enhance accuracy in diagnosis. In the NIH study, they found that the average number of biopsy specimens per procedure was 38.2, showing how meticulous and exact you can be with endoscopic methods.
This operation aids in speedier recovery and shorter periods for getting back biopsy results, assisting with quick diagnosis and planning of treatment. The NIH study highlighted that even with a high number of biopsies, the risk of complications did not increase, underscoring the efficiency and reliability of endoscopic biopsies.

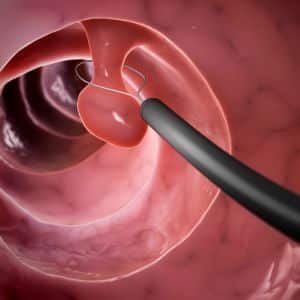
What are the risks and complications of endoscopic biopsies?
Endoscopic biopsies, known for their less invasive nature, have some unique benefits compared to surgeries for biopsy. They require smaller cuts that result in less pain and a faster healing process among patients. The application of endoscopes enables accurate and immediate viewing of the area being targeted, thus ensuring that tissue samples are collected with utmost care from areas showing potential problems or suspicion. This ability does not just improve the precision of diagnosis, it also decreases the chances of missing out on pathological areas like in conventional manners.
Regarding complications, endoscopic biopsies generally exhibit lower rates than surgical procedures. Minor bleeding at the place where a biopsy is done is normal however in the study of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) there were limited cases of minor bleeding.
Infection, even though it happens very rarely, remains a possible risk that can normally be handled well with antibiotics which also reinforces its safety characteristic.
Misalignment or accidental perforation is a serious concern, but it happens very rarely during endoscopic biopsies. Patients might feel some temporary discomfort or tenderness where the endoscope was conducted, and there could be a chance for negative reactions to sedatives or anaesthetics used during this process. Nonetheless, these discomforts are usually slight and temporary. They add to the patient's favourable experience linked with endoscopic biopsies.
Endoscopic biopsies are a big step forward in diagnostic processes. They provide better safety, precision and comfort to the patient when compared with old-fashioned biopsy methods. The results of thorough studies like those done at NIH highlight its efficiency and trustworthiness in clinical use which encourages more doctors from different medical fields to use this method extensively.
FAQs
Symptoms such as persistent abdominal pain, unexplained weight loss, difficulty swallowing, persistent heartburn, or changes in bowel habits may indicate the need for an endoscopic biopsy to investigate underlying gastrointestinal conditions.
You may experience mild discomfort, such as bloating or a sore throat, which usually resolves quickly. Your doctor will provide post-procedure care instructions tailored to your needs.
By obtaining tissue samples directly from the gastrointestinal tract, an endoscopic biopsy can provide crucial diagnostic information to identify the cause of symptoms, guiding appropriate treatment decisions.
Consult a gastrointestinal specialist for an endoscopic biopsy
Ready to get clarity on your gastrointestinal health? Consult a gastrointestinal specialist today for an endoscopic biopsy.
To find out what's causing your gastrointestinal conditions, you need precision and skill. A gastroenterologist who specialises in this area can give reliable information about conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease, coeliac disease, or even early signs of gastrointestinal cancers.
Do not wait for the symptoms to get worse; be proactive in taking steps towards better health by making an appointment for your consultation about a biopsy today. Your health deserves the best — contact us today to schedule your appointment for an endoscopic evaluation.
